Homework 12 - The Runge-Kutta ODE Solver
There exist many different ODE solvers. To demonstrate how we can get significantly better results with a simple update to Euler, you will implement the second order Runge-Kutta method RK2:
RK2 is a 2nd order method. It uses not only RK2 computes an initial guess 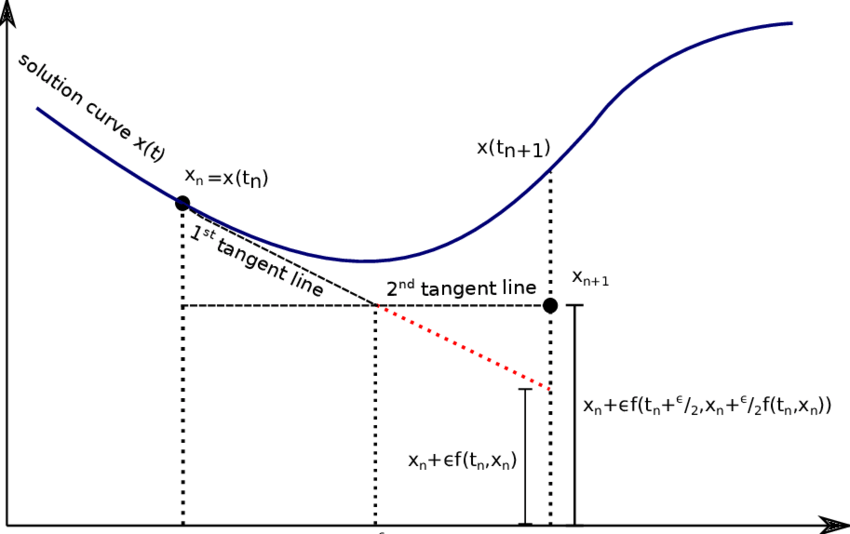
The code from the lab that you will need for this homework is given below. As always, put all your code in a file called hw.jl, zip it, and upload it to BRUTE.
struct ODEProblem{F,T<:Tuple{Number,Number},U<:AbstractVector,P<:AbstractVector}
f::F
tspan::T
u0::U
θ::P
end
abstract type ODESolver end
struct Euler{T} <: ODESolver
dt::T
end
function (solver::Euler)(prob::ODEProblem, u, t)
f, θ, dt = prob.f, prob.θ, solver.dt
(u + dt*f(u,θ), t+dt)
end
function solve(prob::ODEProblem, solver::ODESolver)
t = prob.tspan[1]; u = prob.u0
us = [u]; ts = [t]
while t < prob.tspan[2]
(u,t) = solver(prob, u, t)
push!(us,u)
push!(ts,t)
end
ts, reduce(hcat,us)
end
# Define & Solve ODE
function lotkavolterra(x,θ)
α, β, γ, δ = θ
x₁, x₂ = x
dx₁ = α*x₁ - β*x₁*x₂
dx₂ = δ*x₁*x₂ - γ*x₂
[dx₁, dx₂]
endlotkavolterra (generic function with 1 method)Implement the 2nd order Runge-Kutta solver according to the equations given above by overloading the call method of a new type RK2.
(solver::RK2)(prob::ODEProblem, u, t)You should be able to use it exactly like our Euler solver before:
using Plots
using JLD2
# Define ODE
function lotkavolterra(x,θ)
α, β, γ, δ = θ
x₁, x₂ = x
dx₁ = α*x₁ - β*x₁*x₂
dx₂ = δ*x₁*x₂ - γ*x₂
[dx₁, dx₂]
end
θ = [0.1,0.2,0.3,0.2]
u0 = [1.0,1.0]
tspan = (0.,100.)
prob = ODEProblem(lotkavolterra,tspan,u0,θ)
# load correct data
true_data = load("lotkadata.jld2")
# create plot
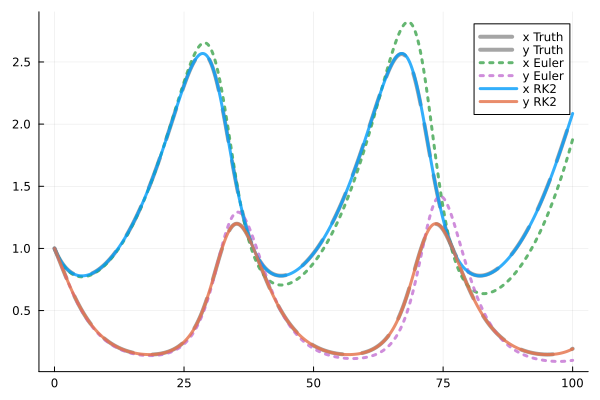
p1 = plot(true_data["t"], true_data["u"][1,:], lw=4, ls=:dash, alpha=0.7,
color=:gray, label="x Truth")
plot!(p1, true_data["t"], true_data["u"][2,:], lw=4, ls=:dash, alpha=0.7,
color=:gray, label="y Truth")
# Euler solve
(t,X) = solve(prob, Euler(0.2))
plot!(p1,t,X[1,:], color=3, lw=3, alpha=0.8, label="x Euler", ls=:dot)
plot!(p1,t,X[2,:], color=4, lw=3, alpha=0.8, label="y Euler", ls=:dot)
# RK2 solve
(t,X) = solve(prob, RK2(0.2))
plot!(p1,t,X[1,:], color=1, lw=3, alpha=0.8, label="x RK2")
plot!(p1,t,X[2,:], color=2, lw=3, alpha=0.8, label="y RK2")